3 Types of Emulsions
An example of a temporary emulsion is a simple vinaigrette while mayonnaise is a permanent emulsion. Emulsion-breaking products are designed to break water-in-oil emulsions.

Types Of Emulsifiers How Homogenization Creates Stable Emulsions
Read customer reviews best sellers.

. There are three kinds of emulsions. 13 Emulsions can increase the amount of waste material to be collected by up to three times the volume of oil spilled. Emulsions and Suspensions are two special types of solutions.
MDGs are the most commonly used food emulsifiers composing about 75 of total emulsifier. Butter and cold cream are typical examples of this types of emulsions. In this article we will study the distinct properties of emulsions and suspensions components types and.
Semi-Permanent - Hold longer than temporary emulsions. Ad Browse discover thousands of unique brands. What is emulsion give two examples.
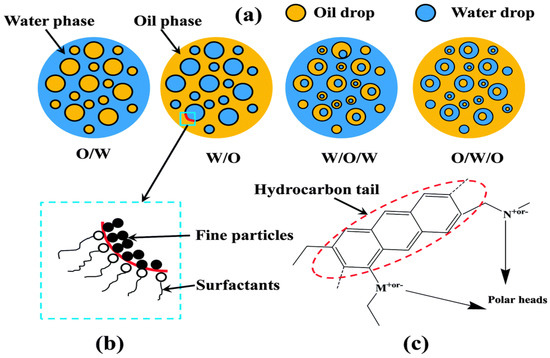
Amphiphilic surfactants can be catagorised by the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance HLB which is a relative ratio of polar and non-polar groups in particular surfactant. Examples of emulsions include mayonnaise milk lotions etc. Emulsions are characterized as follows based on the nature of the dispersed phase.
Butter and cold cream are typical examples of this types of emulsions. Typically if the oil is dispersed phase the emulsion. However depending upon the need more complex systems referred to as double emulsions or multiple emulsions in which the oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsions are.
In this way. Oil-in-water emulsions are common in food products. Also what type of emulsion is cream.
The amount of demulsifier required depends on the. Emulsions and Suspensions are colloidal solutions. An example of a temporary emulsion is a simple vinaigrette while mayonnaise is a permanent emulsion.
Other types of emulsions include butter which is a water-in-fat emulsion and egg yolks with lecithin. Examples include butter margarine homogenized milk mayonnaise etc. These emulsion are also termed oil emulsions.
What are 3 types of food emulsions. Emulsions consist of three components. On the basis of the nature of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium two types of macroemulsions can be distinguished.
They find use in a wide array of food products Table 3. Such an ow emulsion is generally formed if the aqueous phase constitutes more than 45 of the. Classification of oil emulsions.
There are two basic types of emulsions. 1 to 35. Emulsions are the type of a more common class of two-phase systems of matter called Colloids.
Temporary semi-permanent and permanent. An example of a temporary emulsion is a simple vinaigrette while mayonnaise is a permanent emulsion. The three types of emulsion are display ed in Fig1.
An oil-in-water emulsion is one in which oil serves as the dispersed phase and water serves as the dispersion. Although at times the terms colloid and emulsion are often used interchangeably. Oil representing hydrocarbon or organic liquids water including any aqueous mixtures and surfactants.
One may also ask what type of emulsion is cream. They are non-homogenous types of solutions. An emulsion is a type of colloid formed by combining two.
The most commonly used food emulsifiers include MDGs stearoyl lactylates sorbitan esters polyglycerol esters sucrose esters and lecithin. These emulsion are also termed oil emulsions. I If the continuous phase is an aqueous solution and the dispersed phase an oil the system is called an ow emulsion.
Temporary semi-permanent and permanent. What are 3 common emulsifiers used in the kitchen. 36 They are usually more soluble in water than in oil although the commercial products available have a wide range of solubility.
The process of formation of an emulsion is termed emulsification. Temporary semi-permanent and permanent. Temporary - Dont hold long after emulsifying.
Vinaigrettes made with mustard. They have a wide range of applications in the chemical and paint industry. These types of emulsions help in delayed release of certain small compounds used in the pharmaceutical industry.
There are three kinds of emulsions. There are three kinds of emulsions. In Healthcare Many cosmetic and pharmaceutical dosage forms are in the form of emulsions.
Depending on the ratio of these components oil-in-water emulsions or water-in-oil emulsions can exist. Cosmetics such as lotions creams biphasic makeup removers are in fact emulsions. Permanent - Hold indefinitely once made.
The word emulsion can be used only when both of the phases are in a liquid state.
Processes Free Full Text The Formation Stabilization And Separation Of Oil Ndash Water Emulsions A Review Html

Emulsion An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Emulsion Emulsifying Agent Types Properties Examples

Llustration Of The 4 Emulsion Systems W O O W W O W And O W O Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment